Februari . 01, 2025 02:33 Back to list
power cable connector types
Electric cable wires, often regarded as the veins of modern infrastructure, play a pivotal role in powering homes, industries, and even the digital ecosystem. Understanding the different types of electric cable wires is crucial for making informed decisions, ensuring safety, and optimizing performance. Delving into this subject unveils insights based on years of technical expertise and professional experience, presenting both common and specialized cable types.
Specialty cables include fiber optic cables and coaxial cables, crucial in the realm of telecommunications and broadcasting. Fiber optic cables, characterized by their ability to transmit data at the speed of light, have revolutionized internet connectivity and communication industries. Coaxial cables, on the other hand, are widely used in cable television and internet services, known for their capacity to carry high-frequency signals with minimal loss. Eco-friendly cables are increasingly significant as industries shift towards sustainable practices. These cables are constructed from halogen-free materials, minimizing environmental impact and enhancing safety by reducing harmful emissions during a fire. This trend reflects the evolving landscape where technological advancement aligns with environmental stewardship. Sizing is another critical aspect. Electric cables come in myriad sizes, each catering to specific current capacities and distance requirements. Oversizing results in unnecessary costs, while undersizing can be hazardous, leading to overheating and potential failures. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of cable sizing is essential for optimal installation and operation. Recent advancements also see the inclusion of smart cables, embedded with sensor technology to monitor performance, detect faults, and facilitate predictive maintenance. These innovations are gradually transforming infrastructure management, offering greater reliability and operational insights. The European and American markets further illustrate regional differences in cable design standards. European cables often adhere to the stringent IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, focusing on uniformity and safety, whereas the American market follows NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines, emphasizing robustness and compatibility with local infrastructure. Navigating the diverse world of electric cable wires requires a balance of technical knowledge and practical application. From choosing the right type and material to considering environmental factors and industry standards, each decision impacts the overall safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Therefore, investing in understanding these multifaceted aspects promises not just seamless implementation but also longevity and sustainability in electrical installations.
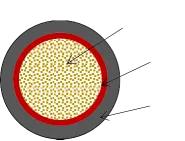

Specialty cables include fiber optic cables and coaxial cables, crucial in the realm of telecommunications and broadcasting. Fiber optic cables, characterized by their ability to transmit data at the speed of light, have revolutionized internet connectivity and communication industries. Coaxial cables, on the other hand, are widely used in cable television and internet services, known for their capacity to carry high-frequency signals with minimal loss. Eco-friendly cables are increasingly significant as industries shift towards sustainable practices. These cables are constructed from halogen-free materials, minimizing environmental impact and enhancing safety by reducing harmful emissions during a fire. This trend reflects the evolving landscape where technological advancement aligns with environmental stewardship. Sizing is another critical aspect. Electric cables come in myriad sizes, each catering to specific current capacities and distance requirements. Oversizing results in unnecessary costs, while undersizing can be hazardous, leading to overheating and potential failures. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of cable sizing is essential for optimal installation and operation. Recent advancements also see the inclusion of smart cables, embedded with sensor technology to monitor performance, detect faults, and facilitate predictive maintenance. These innovations are gradually transforming infrastructure management, offering greater reliability and operational insights. The European and American markets further illustrate regional differences in cable design standards. European cables often adhere to the stringent IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, focusing on uniformity and safety, whereas the American market follows NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines, emphasizing robustness and compatibility with local infrastructure. Navigating the diverse world of electric cable wires requires a balance of technical knowledge and practical application. From choosing the right type and material to considering environmental factors and industry standards, each decision impacts the overall safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Therefore, investing in understanding these multifaceted aspects promises not just seamless implementation but also longevity and sustainability in electrical installations.
Share
Next: