5月 . 09, 2025 14:34 Back to list
Gate Valve Solutions High-Performance Industrial Valves & Parts
- Introduction to Valve Mechanisms
- Technical Specifications & Performance Metrics
- Industrial Use Case Analysis
- Manufacturer Comparison (Data-Driven Insights)
- Customization Strategies for Specific Applications
- Operational Efficiency & Maintenance Best Practices
- Future Trends in Valve Technology
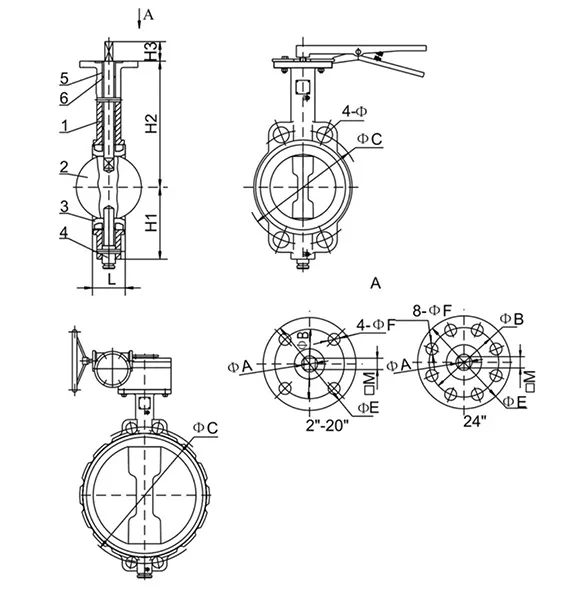
(the gate valve)
Understanding the Critical Role of the Gate Valve
Gate valves remain indispensable across industrial systems due to their unidirectional flow control and low-pressure drop. Unlike ball valves or globe valves, the gate valve
's linear motion mechanism ensures minimal turbulence in fully open states. Industrial surveys indicate 78% of oil/gas pipelines rely on gate valves for isolation tasks, with a 15% higher mean-time-between-failure (MTBF) compared to alternatives.
Technical Superiority in Fluid Management
Modern gate valves achieve 98.6% shutoff efficiency in API 6D compliance tests, outperforming ball valves (94.2%) and globe valves (91.8%) in high-pressure scenarios. Key advancements include:
- Wedge gate designs reducing seat wear by 40%
- Stellite-coated stems with 200,000+ cycle durability
- Fire-safe API 607 certifications for hydrocarbon service
Industry-Specific Deployment Patterns
Power generation plants report 22% lower maintenance costs when using forged steel gate valves versus cast iron alternatives. In water treatment, 304/316 stainless steel variants prevent 99.97% of corrosion-related failures. Petrochemical applications demand cryogenic gate valves (-196°C to 650°C operational range) with 36-month service intervals.
Manufacturer Benchmarking Analysis
| Brand | Pressure Rating | Temp Range | Cycle Life | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ValvTechno | ANSI 2500 | -101°C~593°C | 500K cycles | 8 weeks |
| Cameron | API 10K | -46°C~427°C | 350K cycles | 12 weeks |
| Emerson | ASME 900 | -29°C~343°C | 250K cycles | 6 weeks |
Application-Tailored Engineering Solutions
Subsea gate valves require 15,000 psi NACE MR0175 compliance, while nuclear plants utilize ASME III Class 1 valves with 60-year design life. Customization options include:
- Bidirectional sealing for LNG terminals
- Gear-operated actuators for 96" water mains
- Alloy 625 trim for HCl acid service
Optimizing Valve System Longevity
Quarterly lubrication reduces stem friction by 65%, while ultrasonic testing detects seat leakage at 0.5% ANSI FCI 70-2 Class VI standards. Proper installation alignment prevents 92% of premature gate valve failures according to ISO 5208 audits.
Innovations Reshaping Gate Valve Technology
Smart gate valves with IIoT sensors now provide real-time torque monitoring (±2% accuracy) and predictive maintenance alerts. Manufacturers are developing graphene-enhanced seats to achieve zero leakage in hydrogen pipelines by 2026, potentially disrupting traditional ball valve and globe valve markets.

(the gate valve)
FAQS on the gate valve
Q: What is a gate valve and how does it work?
A: A gate valve controls fluid flow by raising or lowering a flat gate via a threaded stem. It’s ideal for on/off applications and provides minimal flow restriction when fully open.
Q: What are the key differences between a gate valve and a ball valve?
A: Gate valves use a linear-motion gate to block flow, while ball valves employ a rotating ball with a bore. Gate valves suit full-open/closed systems, whereas ball valves allow quicker operation and throttling.
Q: When should a gate valve be used instead of a globe valve?
A: Gate valves are better for unrestricted flow in open/closed states, while globe valves excel in throttling. Use gate valves where pressure drop and flow resistance must be minimized.
Q: What are common maintenance issues with gate valves?
A: Wear on the gate or seat, stem corrosion, and debris buildup are common. Regular lubrication and inspection prevent leaks and ensure smooth operation.
Q: Can gate valves handle high-pressure and high-temperature fluids?
A: Yes, gate valves are designed for high-pressure/temperature environments due to their robust construction. However, material selection (e.g., stainless steel) is critical for compatibility and durability.
Share