Nov . 06, 2024 01:31 Back to list
Electric Cable and Wire Solutions for Reliable Power Distribution and Connectivity
Understanding Cable and Electric Wire A Comprehensive Overview
In today's world, electricity plays a pivotal role in our daily lives, powering everything from household appliances to large industrial machines. At the heart of this electrification process lies a crucial component cable and electric wire. These two elements form the backbone of electrical infrastructure, enabling the safe and efficient transfer of electricity from one point to another. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between cable and electric wire, their various types, applications, and the importance of selecting the right materials for specific tasks.
Definition and Differences
At its core, electricity requires a pathway to travel through. This pathway is provided by conductive materials, primarily copper or aluminum, encapsulated within protective coverings. While the terms cable and wire are often used interchangeably, they refer to different structures.
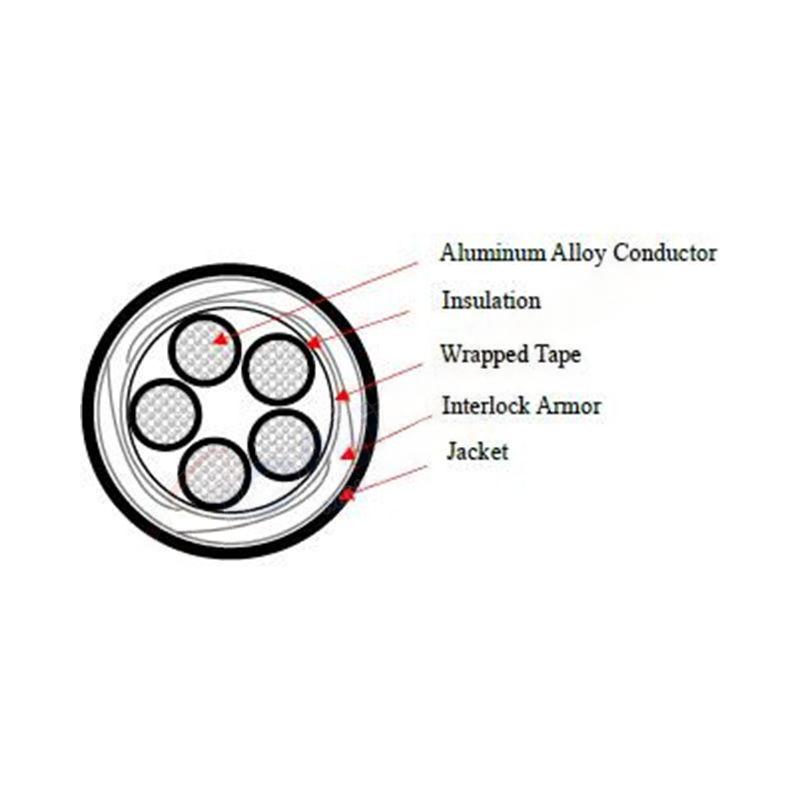
A wire generally refers to a single conductor that can be insulated or bare, used to carry electric current. In contrast, a cable consists of multiple wires bundled together in a protective sheath. The grouping allows for further insulation, shielding, and easier installation in various environments. Thus, the primary difference lies in the construction and application wire is typically for less complex electrical installations, while cables are used for more intricate setups requiring multiple conductors.
Types of Cable and Wire
Electric cables and wires come in many types, each designed for specific applications
. Some common examples include1. Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable (Romex) Commonly used in residential wiring, this cable type consists of three to four insulated wires surrounded by a plastic sheath. Romex is cost-effective and easy to handle.
2. Conductors These are typically bare or insulated wires, known for carrying current. They can be solid or stranded for flexibility. Solid conductors are often used in stationary applications, whereas stranded conductors are favored where movement occurs.
3. Armored Cable (AC) Typically used in commercial applications, AC is designed with a protective metal sheath that guards against physical damage and moisture. It is ideal for environments where wires are exposed to potential hazards.
cable electric wire
4. Coaxial Cable Widely used in telecommunications and data transmission, coaxial cable consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and a conductive shield, making it perfect for carrying high-frequency signals with minimal interference.
5. Fiber Optic Cables While not an electrical wire in the traditional sense, fiber optic cables are essential for modern communication. They use light to transmit data over long distances, offering higher speeds and greater bandwidth compared to traditional cables.
Applications
The applications of cables and electric wires are virtually limitless. In residential settings, they are used for basic lighting and power outlets. In commercial environments, they facilitate the operation of machinery, HVAC systems, and lighting. In industrial sectors, robust cables are crucial for the functioning of heavy equipment and safety systems.
The telecommunications industry heavily relies on various types of cables for internet, television, and telephone services. Additionally, power distribution networks utilize high-voltage cables to transport electricity from generation plants to end-users.
Importance of Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the appropriate cable or wire for a specific use case is vital for both safety and efficiency. Factors such as the amperage rating, insulation type, environmental exposure, and installation method must be considered. Using cables and wires that are not suited for the application can lead to overheating, short circuits, or even electrical fires.
Moreover, compliance with local electrical codes and regulations is critical when installing or replacing electrical components. Professionals often refer to established standards and guidelines to ensure safety and reliability in wiring practices.
Conclusion
In summary, the importance of cables and electric wires cannot be overstated in the electrical world. Their varying types and applications underscore the essential role they play in powering our lives. Understanding the distinction between cables and wires, along with their appropriate uses, can lead to safer, more efficient electrical systems. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, the careful selection and installation of these components lay the groundwork for reliable electricity distribution, ultimately enhancing our quality of life in the modern age.
Share
-
Reliable Wafer Type Butterfly Valves for Every IndustryNewsJul.25,2025
-
Reliable Flow Control Begins with the Right Ball Check ValveNewsJul.25,2025
-
Precision Flow Control Starts with Quality ValvesNewsJul.25,2025
-
Industrial Flow Control ReliabilityNewsJul.25,2025
-
Engineered for Efficiency Gate Valves That Power Industrial PerformanceNewsJul.25,2025
-
Empowering Infrastructure Through Quality ManufacturingNewsJul.25,2025