Սպտ . 22, 2024 07:48 Back to list
gate valve non rising
Understanding Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves Key Features and Applications
Non-rising stem gate valves are essential components in various industrial applications, particularly in piping systems that manage the flow of liquids or gases. Unlike traditional rising stem gate valves, which have a visible stem that rises and falls when the valve is operated, non-rising stem gate valves maintain a fixed position, with the gate moving up and down within the valve body. This design offers several advantages and specific applications that make non-rising stem gate valves a popular choice in many industries.
Understanding Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves Key Features and Applications
Non-rising stem gate valves are typically operated through a handwheel or actuator, which engages the stem directly to raise or lower the gate. This operation minimizes the exposure of the inner components to the outside environment, reducing wear and increasing reliability. Additionally, the design of these valves allows for smooth operation, ensuring that the gate seals tightly against the seat, thus preventing leakage.
gate valve non rising
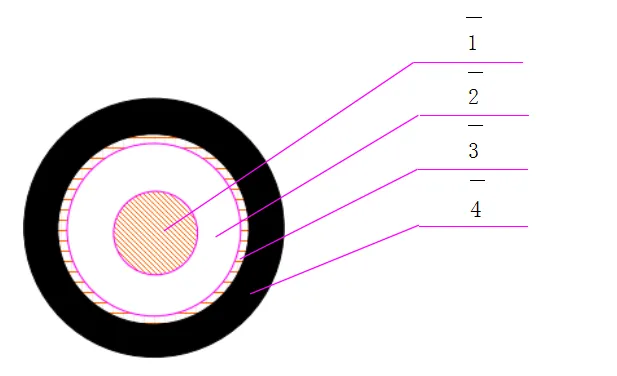
In terms of materials, non-rising stem gate valves are available in a variety of options, including brass, stainless steel, and various alloys. This versatility allows engineers and designers to select the right material based on the specific requirements of the application, such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the fluid being handled. For example, stainless steel valves are often chosen for corrosive environments, while brass valves might be utilized in less demanding applications.
Applications of non-rising stem gate valves are widespread. They are commonly employed in water treatment facilities, oil and gas pipelines, and chemical processing plants. In these contexts, the ability to fully open or close the valve ensures that flow control is efficient and effective. Moreover, their reliability and ease of maintenance make them a favored choice where downtime needs to be minimized.
In conclusion, non-rising stem gate valves offer numerous advantages in terms of design, functionality, and applications. Their compact structure, durability, and reliable sealing capabilities make them indispensable in various industries. As technology advances and industries seek more efficient solutions for fluid management, the relevance of non-rising stem gate valves is likely to grow, ensuring their continued use in modern engineering and infrastructure projects. Understanding these valves and their characteristics is crucial for professionals involved in design and maintenance within fluid control systems.
Share
-
Reliable Wafer Type Butterfly Valves for Every IndustryNewsJul.25,2025
-
Reliable Flow Control Begins with the Right Ball Check ValveNewsJul.25,2025
-
Precision Flow Control Starts with Quality ValvesNewsJul.25,2025
-
Industrial Flow Control ReliabilityNewsJul.25,2025
-
Engineered for Efficiency Gate Valves That Power Industrial PerformanceNewsJul.25,2025
-
Empowering Infrastructure Through Quality ManufacturingNewsJul.25,2025